cytoflow.operations.binning¶
-
class
cytoflow.operations.binning.BinningOp[source]¶ Bases:
traits.has_traits.HasStrictTraitsBin data along an axis.
This operation creates equally spaced bins (in linear or log space) along an axis and adds a condition assigning each event to a bin. The value of the event’s condition is the left end of the bin’s interval in which the event is located.
-
name¶ The operation name. Used to name the new metadata field in the experiment that’s created by apply()
Type: Str
-
channel¶ The name of the channel along which to bin.
Type: Str
-
scale¶ Make the bins equidistant along what scale?
Type: {“linear”, “log”, “logicle”}
-
bin_width¶ The width of the bins. If
scaleislog,bin_widthis in log-10 units; ifscaleislogicle, and error is thrown because the units are ill-defined.Type: Float
Examples
Create a small experiment:
>>> import cytoflow as flow >>> import_op = flow.ImportOp() >>> import_op.tubes = [flow.Tube(file = "tasbe/rby.fcs")] >>> ex = import_op.apply()
Create and parameterize the operation
>>> bin_op = flow.BinningOp() >>> bin_op.name = "Bin" >>> bin_op.channel = "FITC-A" >>> bin_op.scale = "log" >>> bin_op.bin_width = 0.2
Apply the operation to the experiment
>>> ex2 = bin_op.apply(ex)
Plot the result
>>> bin_op.default_view().plot(ex2)
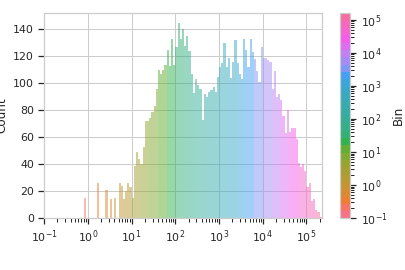
-
apply(experiment)[source]¶ Applies the binning to an experiment.
Parameters: experiment (Experiment) – the old_experiment to which this op is applied Returns: A new experiment with a condition column named name, which contains the location of the left-most edge of the bin that the event is in. Ifbin_count_nameis set, another column is added with that name as well, containing the number of events in the same bin as the event.Return type: Experiment
-
-
class
cytoflow.operations.binning.BinningView[source]¶ Bases:
cytoflow.operations.base_op_views.Op1DView,cytoflow.operations.base_op_views.AnnotatingView,cytoflow.views.histogram.HistogramViewPlots a histogram of the current binning op. By default, the different bins are shown in different colors.
-
channel¶ The channel this view is viewing. If you created the view using
default_view(), this is already set.Type: String
-
scale¶ The way to scale the x axes. If you created the view using
default_view(), this may be already set.Type: {‘linear’, ‘log’, ‘logicle’}
-
op¶ The
IOperationthat this view is associated with. If you created the view usingdefault_view(), this is already set.Type: Instance(IOperation)
-
xfacet, yfacet Set to one of the
conditionsin theExperiment, and a new row or column of subplots will be added for every unique value of that condition.Type: String
-
huefacet¶ Set to one of the
conditionsin the in theExperiment, and a new color will be added to the plot for every unique value of that condition.Type: String
-
plot(experiment, **kwargs)[source]¶ Plot the histogram.
Parameters: - experiment (Experiment) – The
Experimentto plot using this view. - title (str) – Set the plot title
- xlabel, ylabel (str) – Set the X and Y axis labels
- huelabel (str) – Set the label for the hue facet (in the legend)
- legend (bool) – Plot a legend for the color or hue facet? Defaults to True.
- sharex, sharey (bool) – If there are multiple subplots, should they share axes? Defaults to True.
- row_order, col_order, hue_order (list) – Override the row/column/hue facet value order with the given list. If a value is not given in the ordering, it is not plotted. Defaults to a “natural ordering” of all the values.
- height (float) – The height of each row in inches. Default = 3.0
- aspect (float) – The aspect ratio of each subplot. Default = 1.5
- col_wrap (int) – If xfacet is set and yfacet is not set, you can “wrap” the subplots around so that they form a multi-row grid by setting col_wrap to the number of columns you want.
- sns_style ({“darkgrid”, “whitegrid”, “dark”, “white”, “ticks”}) – Which seaborn style to apply to the plot? Default is whitegrid.
- sns_context ({“paper”, “notebook”, “talk”, “poster”}) – Which seaborn context to use? Controls the scaling of plot elements such as tick labels and the legend. Default is talk.
- despine (Bool) – Remove the top and right axes from the plot? Default is True.
- min_quantile (float (>0.0 and <1.0, default = 0.001)) – Clip data that is less than this quantile.
- max_quantile (float (>0.0 and <1.0, default = 1.00)) – Clip data that is greater than this quantile.
- lim ((float, float)) – Set the range of the plot’s data axis.
- orientation ({‘vertical’, ‘horizontal’})
- num_bins (int) – The number of bins to plot in the histogram. Clipped to [100, 1000]
- histtype ({‘stepfilled’, ‘step’, ‘bar’}) – The type of histogram to draw. stepfilled is the default, which is a line plot with a color filled under the curve.
- density (bool) – If True, re-scale the histogram to form a probability density function, so the area under the histogram is 1.
- linewidth (float) – The width of the histogram line (in points)
- linestyle ([‘-’ | ‘–’ | ‘-.’ | ‘:’ | “None”]) – The style of the line to plot
- alpha (float (default = 0.5)) – The alpha blending value, between 0 (transparent) and 1 (opaque).
- color (matplotlib color) – The color to plot the annotations. Overrides the default color cycle.
- experiment (Experiment) – The
-